

Why care for all?

— "From the cradle to the grave"
— Demographic transitions (aging in richer countries, high fertility in poorer countries), health transitions, rapid urbanization, increased female labor force participation, and longer schooling are all changing family caregiving
— Care for the caregivers
Care need in 2030 would require the equivalent of 1/5 to 2/5 of the paid labor force.
If all family caregivers were paid, a value equivalent to 16 to 32 percent of GDP per country (King, Randolph, Floro & Suh (2021))
The care burden in families is not equally shared:
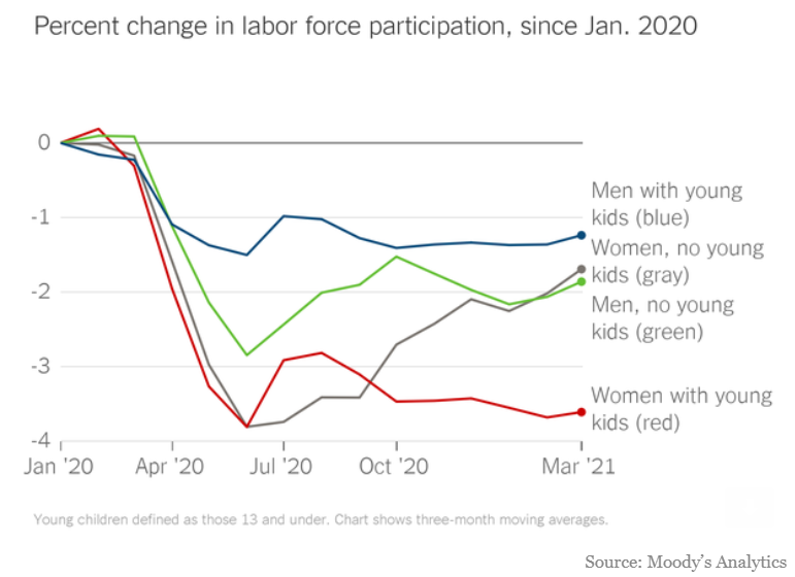
This figure shows the percent change in labor force participation, since January of 2020 and demonstrates the toll of caregiving to caregivers: all groups suffered as a result of the pandemic, but women with young kids (red) have sustained losses in labor force participation.
Measurement and analysis of care burden

— CTMS 2018 household and provider surveys
— Cha (2021) "Determinants Of Paid Elder Care Service Use: Focusing On The Characteristics Of Family Caregiver And Their Household"
— Moon (2021) "The Current Status And Alternatives Of Male Care Participation In Korea"
— Kim (2021) "Policy Recommendations For A High Road To Care In Korea"
— Jun, King, & Kang (2021) "Care Needs Care: Care Needs For Family Caregivers Of The Elderly"
— Peng & Jun (2021) "Impacts Of COVID-19 On Work-Family Balance In South Korea"
— Cha & Moon (2020) "A Glimpse of the Context of Family Caregivers: Actual Time vs. Preferred Time for Elderly Care"
— Friar (2021) "Caring About Influence: Analyzing Relationships and Networks to Promote Effective Advocacy on Care"
— Jun & King (2020); Hensly, Jun & King (2021) "The toll and reward of family caregiving: Eldercare in South Korea"
— Time-use survey data, combined with household survey data; domestic and paid caregivers, ability to distinguish between paid and unpaid services rendered
— King, Randolph, & Suh (2021) "Who cares and who shares? Caregiving in the household"
— Meurs, Tribin Floro, & Lefebvre (2020) "Prospects for Gender-Sensitive Macroeconomic Modelling for Policy Analysis in Colombia: Integrating the Care Economy"
— Donehower & Kye (2021) "Care Support Ratios in Korea and the US"
— Suh, King, Floro & Meurs (2021)
— Macroeconomic models
— Lofgren, Kim & Fontana (2020) "A Gendered Social Accounting Matrix for South Korea"
— Meurs, Tribin Floro, & Lefebvre (2020) "Prospects for Gender-Sensitive Macroeconomic Modelling for Policy Analysis in Colombia: Integrating the Care Economy"
Individuals, families, & communities

"Unpaid caregiving, including child and elder care, care for ill or disabled family members, and household tasks such as cooking and cleaning, is a significant household activity in all countries, yet policies related to employment promotion and poverty reduction are often made without considering the impact of such activities. The still-prevailing belief is that care work is primarily a family duty and responsibility and of little direct relevance to economic development. This neglect ignores the realities that households face: the unequal burden of care withinhouseholds, the impact on girls and women who bear the brunt of that burden, and the limited capability of low-resource households to provide adequate care for their members. Unpaid care work is critical, but remains “invisible."
The COVID-19 pandemic has put a spotlight on unpaid caregiving in the home. When public and private services are shut down or incapacitated, the ability of household members to care for one another becomes our sole option for comfort and even survival. Understanding the magnitude of future care need is a first step in planning for adequate caregiving in countries and for ensuring that that need is met." [King, Randolph, Floro and Suh, 2021]
Topics covered by the research
- Understanding the burden of family caregiving: who cares, who shares
- Forecasting future demand for care
- Psychic/mental, physical & opportunity costs and the quality of life of caregivers
- Role of social and gender norms, relative to market incentives and policies
- Access to affordable, good-quality paid caregiving
Project Research

Miller & Bairoliya (2020) "Parental Caregiving and Household Power Dynamics": Paper | Policy Brief
Kang, Eun, & Jun (2021) "Care Arrangement and Caregiving Activities in South Korea: An Analysis of the Care Work Family Survey on Childcare and Eldercare": Paper | Policy Brief
Suh (2021) "Estimating the Unpaid Care Sector in South Korea": Paper | Policy Brief
Gonzalez Garcia, Seo, & Floro (2020) "Norms, Gender Wage Gap, and Long-Term Care"
Moon & Cha (2021) "Family Caregivers' Elder Care: Understanding Their Hard Time and Care Burden"
Hensly, Jun & King (2021) "The Toll and Reward of Family Caregiving: Eldercare in South Korea"
Cha, Kang, & Floro (2021) "Perceived Unmet Demand for Care in South Korea"
Donehower & Kye (2021) "Care Support Ratios in Korea and the US"
King, Randolph, & Suh (2021) "Who Cares and Who shares? Caregiving in the Household"
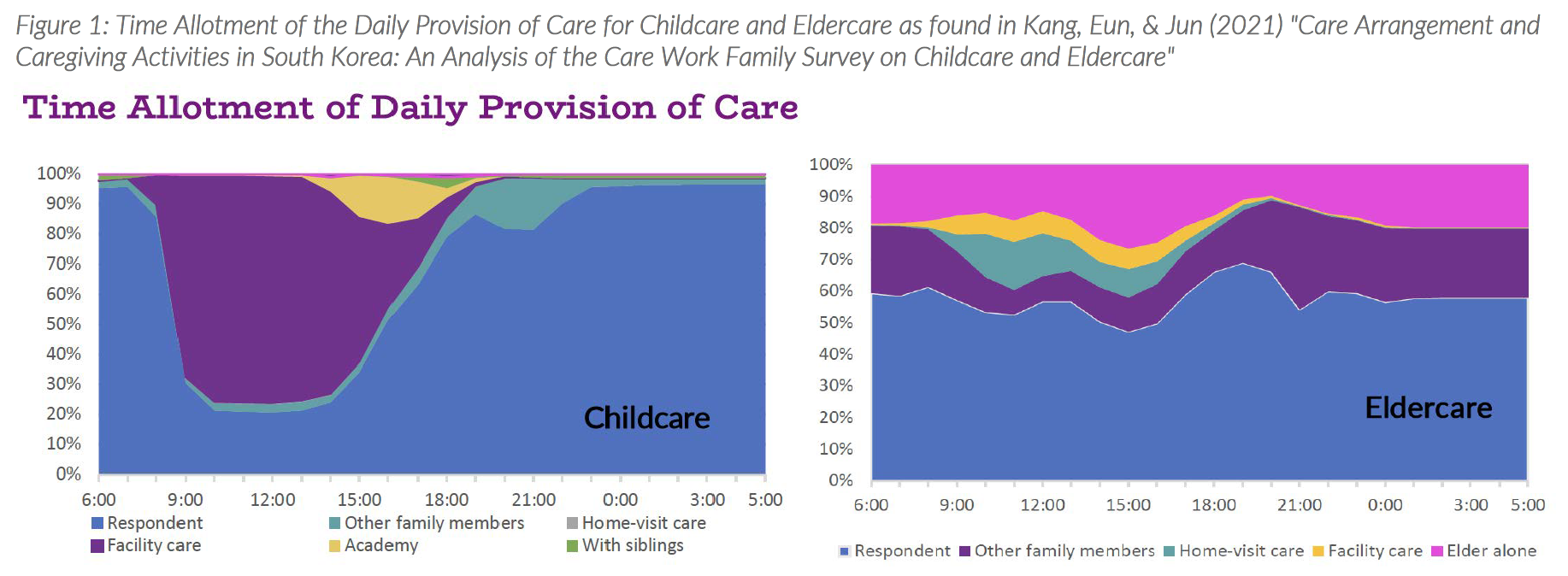
Figure 1 shows the "majority of children are enrolled in facility-based care during the day, but this proportion starts to fall drastically after 3 pm and with a replacement of care by mothers. Likewise, eldercare is concentrated on a primary caregiver in a family. There is a need for public efforts to enhance the equitable share of care works among family members."
Figure 1 can be found in the policy brief for Kang, Eun, & Jun (2021) "Care Arrangement and Caregiving Activities in South Korea: An Analysis of the Care Work Family Survey on Childcare and Eldercare"
CWE-GAM Communications Team 2021


