“Girly Issues” Are Now the Country’s Issues
Dr. Nancy Folbre, an Advisor and Researcher of the CWE-GAM project and a groundbreaking feminist economist was among the first to sound the alarm about the care crisis. Dr. Folbre’s work on the care sector, once considered “just girly issues” by fellow economists, are now recognized as issues belonging to the U.S.. Previously the recipient of the 1998 MacArthur “genius” grant, Dr. Folbre’s research has journeyed from “fringe idea to more mainstream policy.”
Once cast aside in policy discussions, the care crisis is finally getting the spotlight it deserves after the pandemic forced many schools and child-care centers to close, leaving “ten million mothers of school-age children out of the workforce.” The pandemic is forcing policymakers to finally face the cracks in America’s care infrastructure that Dr. Folbre and other experts have long pointed out— “a system where working parents do not have reliable, affordable child care is one where they cannot reliably build a career.”
To learn more about Dr. Folbre’s work on care, visit her blog Care Talk and read her recent book The Rise and Decline of Patriarchal Systems.
This blog was authored by Lucie Prewitt, a research assistant for the CWE-GAM project.
- Published in Child Care, COVID 19, Economic Recovery, Feminist Economics
Making Care Count
The COVID-19 pandemic has informed our understanding of the care economy, exposing disproportionate inequities that must be addressed to alleviate the international erasure of care workers. These issues are addressed in the latest Susan and Michael J. Angelides Lecture, in which Naomi Klein moderates a discussion between Congresswoman Pramila Jayapal and CWE-GAM researcher Dr. İpek İlkkaracan on COVID-19 and the care economy.
We live in an economic system that has traditionally deprioritized and invisibilized care workers, many of which are women of color, migrant, and poor women. The economic crisis brought on by the pandemic has consequently given policymakers and academics “a once-in-a-generation opportunity to address [the valuation of care work] from an intersectional [approach],” states Congresswoman Jayapal.
The Care Crisis Exposed by the Pandemic Recession:
When mass unemployment hit during the pandemic, the cracks in the economic infrastructure of America began to show. As millions of people lost their jobs, the highest increase in the number of uninsured Americans was subsequently recorded. This high number of uninsured people is a direct consequence of healthcare being employer-sponsored. Congresswoman Jayapal notes that “Medicare For All would have strengthened the response to the pandemic…30 percent of COVID-19 deaths were related to a lack of insurance.”
While gains were made in the past decade in regards to gender equality in the workplace, Congresswoman Jayapal notes that “as soon as the pandemic hit, it was the women who went back to taking care of [their] families.” Dr. İpek İlkkaracan explains that this is because “the nature of women’s employment is often determined by their care responsibilities…unpaid care work is often articulated as one of the most significant barriers to labor force participation.” This notion was reflected in jobs reports—in December of 2020, women accounted for 100 percent of job loss, and within that, 154,000 Black women exited the workforce.
In its current state, the care economy produces a pattern of inequality that disproportionately affects women of color and migrant women. The average caregiver salary is $12.74, and the care work sector is marked by poor working conditions with no adequate social protections and low wages. This is why, as Congresswoman Jayapal notes, the fight for one fair wage is pertinent. “An increase in the minimum wage would give 32 million workers a raise, 60 percent of which are women while 1 in 4 of the women who would benefit from this increase are Black or Latina.”
A Framework for a More Caring Economy:
Dr. İpek İlkkaracan has developed a framework that acknowledges the care economy. This framework, coined as the Purple Economy (a nod to the color representative of many women’s movements), envisions a gender-egalitarian and caring economic system. Dr. İlkkaracan recommends “labor market regulations and investment in care services such as long-term care, early childhood education, education, and healthcare” as policy interventions to start the process of adequately valuing care.
Not only is investment in care important from a humanitarian and ethical perspective, but it is also conducive to economic stability. Dr. İlkkaracan’s research has revealed that investment in care services produces a high employment multiplier: for every dollar invested in care, three times as many jobs are created in the wider economy. This is because the care sector is intertwined with other sectors such as food, transport, and financial services. In the Asia-Pacific region, Dr. İlkkaracan’s research has shown that “up to four trillion dollars could be added to GDP if unpaid care work (75% of which done by women) was valued in market terms.” While this may seem astronomical, the amount of unpaid work completed globally in one day equates to 16.4 billion hours—which translates to two billion full-time jobs. Dr. İlkkaracan’s recent research also reveals that a “3.5-4% commitment of GDP to investment in care services would create 120 million additional jobs and have a large impact on poverty alleviation.”
To watch the full conversation and learn more about the Purple Economy, see below.
Dr. İpek İlkkaracan is a CWE-GAM researcher a part of the Rethinking Macroeconomics and Gender Aware Applied Economics Working Groups.
This blog was authored by Lucie Prewitt, a research assistant for the CWE-GAM project.
- Published in Child Care, COVID 19, Economic Recovery, Gender-Equal Economy, Policy, Rethinking Macroeconomics, U.S.
Systemic Resilience and Carework: An Asia-Pacific Perspective
Below is an excerpt from a recent piece “Systemic Resilience and Carework: An Asia-Pacific Perspective” by Ito Peng, contributing researcher for the Understanding and Measuring Care group. This article was published by Migrants and Systemic Resilience: A Global COVID19 Research and Policy Hub (Mig-Res-Hub).
In this think-piece I consider how we can build a resilient systemic response to the COVID-19 pandemic and future crises. I focus on systemic resilience in relation to carework and global migration of careworkers, and I approach this from an Asia-Pacific perspective. One of the fault lines exposed by the COVID-19 is the vulnerability of the existing care, carework and migration infrastructure to exogenous shocks. Asia-Pacific is an important site to examine because it is one of the major sites of global care migration, both as sender and receiver of migrant careworkers. This think-piece draws on the research from our global partnership project based at the University of Toronto, which looks at the dynamics of careworker migration in Asia-Pacific and the interconnections between social and economic forces and policies in shaping those dynamics from both sending and receiving country perspectives. The next section briefly outlines the pandemic’s impacts on carework and care migration in Asia-Pacific. I then discuss how we might achieve systemic resilience in global care migration by first emphasizing how our care systems are interlocked with the global migration of careworkers (what I call a global care interlock), and second, how we might achieve systemic resilience. Understanding the global care interlock is an important prerequisite to systemic resilience because it allows us to see carework and migration of careworkers as a part of a larger global infrastructure or ecosystem that has been, consciously or unconsciously, built, managed and sustained by multiple actors in different parts of the globe.
Read the entire article here.
This blog was authored by Ito Peng, contributing research for the Understanding and Measuring Care research group.
- Published in Asia-Pacific, Child Care, COVID 19, Elder Care, Migrant Care Workers, Understanding and Measuring Care
Macroeconomic Policies, Care and Gender in the Post-COVID Era: Part II
Faculti, an organization that presents digital media from leading experts and academics outlining their work, recently released a digital presentation by the Care Work and the Economy Principal Investigator Dr. Maria S. Floro entitled “Macroeconomic Policies, Care and Gender in the Post-COVID Era.” The discussion describes the interconnections between the crisis of care, the deepening ecological crisis and growth and accumulation processes.
There are many common threads with the climate and ecological crisis and the care crisis. Significantly, the idea that economic growth is overall beneficial. The type of economic growth generally pursued worldwide has not only increased stresses put upon the earth’s resource base but also on care labor capacity, which is similarly but wrongly perceived to be of infinite supply. Moreover, arguments that equate economic growth with overall improvement fail to recognize the distributional element of rising income inequality, which is far more nuanced. In fact, among countries that are higher income, gains from economic growth within those nations do not trickle down to everyone. When looking at care, the widening income equality gaps has shifted distribution of care givers across social classes and national boundaries. As a result, the quality and adequacy of care within a single nation can be very different, which exacerbates differences in social reproduction.
At the same time, income inequality has created a solution for the care needs of those that have the means to hire care for children and elderly, because care workers in those sectors are often paid low wages. But for the working poor, hiring care work help is inaccessible due to financial constraints, therefore they rely on their kinship networks to help provide this care. Furthermore, much of the care work burden still falls on women even as they enter to labor force. Economics and social policy in many parts of the world continue to neglect the heavy work burden put upon women and the necessity to balance household care activities and market work. What can also be observed is a global care supply chain, with the migration of women and girls to urban areas to provide care for wealthier families. Care itself is becoming one of the drivers of income inequality.
The economy is not all about material production; it is really about human vision and social provisions. However, an illusion has been created that unpaid care work is a natural resource that serves as an input for market production to promote GDP growth. However, this idea does not take into account that the wellbeing of people, especially the elderly, the sick and children should be an end in and of itself, to achieve sustainable growth. There is much work to be done to address these issues. To begin, economists must envision long term horizons that look forward to future generations while also taking into account the interdependence of life and moral responsibility. They must also integrate care and environmental consequences into our economic policy tools. Overall a new economic paradigm that includes green ecology and feminist economic concerns is needed.
Link to Part 1 of this blog here.
Macroeconomic Policies, Care and Gender in the Post-COVID Era: Part I
Faculti, an organization that presents digital media from leading experts and academics outlining their work, recently released a digital presentation by the Care Work and the Economy Principal Investigator Dr. Maria S. Floro entitled “Macroeconomic Policies, Care and Gender in the Post-COVID Era.” This discussion delves into the foundation of project itself, its context, the analytical tools utilized in the research, as well as the external factors that have served as the catalyst for the work being done.
The Care Work and the Economy Project was developed after a group of feminist economists observed that in the effort to reduce gender gaps in economic outcomes, as laid out within the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals, there were aspects of care work that needed to be addressed. The project includes 35 scholars from all around the world that are working to develop innovative analytical tools. The research has been applying and testing these tools in South Korea, a country that quickly industrialized in the 70s and 80s and therefore witnessed a very rapid demographic change in fertility and life expectancy.
The care economy, which is inclusive of caring for those that cannot care for themselves, underpins the production of all economies within society. This begins with the fact that if people stopped having children, which require care, then the economy would come to a halt due to lack of labor force. Generally, care work has a tendency to be undermined through a lack of gender awareness in macroeconomic modeling, which does not address care needs in any adequate manner. This aspect is also neglected within the policy making discourse, with the current economic paradigm failing to take into account the necessity for care work to achieve economic growth.
Economic models that display growth also fail to take into consideration social elements, making the assumptions that, for example, children will be cared for despite the lack of social investment into care. However, with care work there comes social, political and economic significance. The Care Work and the Economy project is working to demonstrate what a care focused macroeconomic model can reveal through the implementation of the analytic tools being developed and implemented through the research.
The absence of the care economy within macroeconomic models is in large part due to it being “invisible” since the work often unpaid. This has led to the neglect of care needs despite unpaid care work providing indispensable services in terms of economic activity and growth. The result is an emerging care crisis that has manifested itself in terms of uncared for elderly, sick and children. Furthermore, the crisis has provoked a form of silent protest against long unpaid work hours performed by women, leading to a decline in marriage and fertility rates. This in turn has resulted in a reproduction crisis.
The Care Work and the Economy project researchers are developing and using innovative analytical tools to bring care to the forefront, along with a deeper understanding of the nature of care work, while illustrating the intersectionality between care provisioning, economic growth and distribution. Although these analytical modeling tools are currently being applied in South Korea, the project believes they can be adopted and implemented into other countries as long as the provision of care is taken into context of those countries. The project research shows that governments have an important role and duty to invest in care provisions as well as comprehensive national care plans. One of the key findings is that it is important to take into account demographic change and climate change along with economic and structural changes taking place in policy making. This is a tall order but necessary to sustain economies and provide a future for next generation.
Link to Part 2 of this blog here.
This blog was authored by Jenn Brown, CWE-GAM Communications Assistant
Making the Biden-Harris Economic Recovery Plan Gender Responsive
A recent Gender & COVID-19 brief (also a sign on letter) “Making the Biden-Harris Transition Plan for COVID-19 gender-responsive” outlines how the Biden-Harris Transition Plan in the US can be made more gender-responsive. The brief is a starting point in highlighting the potential within the Biden-Harris Transition Plan, using economic recovery as an entry point, with recommendations based on the best practices for feminist economic recovery from COVID-19.
The Biden-Harris Economic Recovery Plan is constructed around four challenges which must be overcome to rebuild the nation. The brief applies a gender lens for each challenge, emphasizing that for these efforts to be truly equitable, it is critical that they are not implemented in isolation and an intersectional gender lens is used in policy making and interventions.
- Mobilize American manufacturing and innovation to ensure that the future is made in America, and in all of America: Targeted support to business owners from under-represented groups in the forms of emergency funds, skills, training and mentorship; and direct funding to businesses in women-majority sectors, including caregiving and social enterprises, should be a centerpiece of the policy.
- Mobilize American Ingenuity to build a modern infrastructure and an equitable, clean equitable future: Investment in care infrastructure is also green, as it supports jobs for women (in the care sector) and men (in the construction sector), and provides services communities need to thrive. Implementing stimulus programs focused on ‘green jobs’ should proactively plan for gender equity and include formal programming for women, with special emphasis on displaced workers, communities of color, and women who are in recovery from incarceration.
- Mobilizing American talent and heart to build a 21st century caregiving and education workforce: Prioritize universally accessible, free (or highly subsidized) childcare and long-term elder care as central to its economic recovery plan. This can in part be accomplished through the designation of direct public funds to existing regulated and licensed care services. Direct public funds should also be used to invest in measures to keep workers safe and expand the number of care spaces available. Importantly, many workers who provide the backbone of the care economy are informally employed, wherein they have limited or no access to social protection. As such, government assistance schemes should be expanded to include family and informal caregivers, and an expedited path to permanent resident status should be created for precarious immigrant care workers so that they can access those schemes. This has a much greater effect than simply creating employment in the care sector but facilitates women’s participation across the economy.
- Mobilize across the board to advance racial equity in America: There can be no gender justice while there is racial injustice. Racial and gender inequities are inextricably linked to the economy. For example, Black, racialized, and immigrant women are disproportionately represented as personal support workers, cleaners, and in other essential but low-paid occupations – many of which are in the informal economy – that do not provide paid sick leave or family leave.
READ FULL BRIEF: Solomon A, Morgan R, Wenham C, Smith J, Nacif Pimenta D, Mueller V, Herten-Crabb A and Hawkins K (2020) Making the Biden-Harris Transition Plan for COVID-19 gender-responsive, Gender and COVID-19 project
This blog was authored by Jenn Brown, CWE-GAM Communications Assistant
Digital Forum on Reopening Long Island and Building a Fair Economy:Care Work in the COVID Crisis
Earlier this month, the Hofstra Labor Studies and the Center for the Study of Labor and Democracy in collaboration with Long Island Jobs with Justice and A.L.L.O.W. (Advancing Local Leadership Opportunities for Women) conducted a virtual forum addressing care work in the context of COVID-19. This discussion emphasized the financial and mental health challenges associated with all types of care work during this pandemic, and the immense need to address and resolve these issues in order to assist with a fair and sustainable economic recovery. Although the discussion is focused primarily on Long Island and New York, the problems indicated are applicable to care work throughout the U.S.
There is anecdotal evidence to suggest that the unemployment or the stress of juggling work and home life as a result of the crisis has hit women much harder than men. This discussion utilized academia as an example of this, drawing upon data indicating that academic journal submissions have greatly increased among men since the beginning of the pandemic, but sharply decreased among women. For those working in academia, publishing work is crucial to professional advancement.
The pandemic has also shed a harsh light on the fragility of the overall childcare system in the U.S. Many families lacked adequate childcare even before the pandemic, forcing them to rely on unpaid care work. These existing issues paired with the recent closures of childcare facilities has exacerbated the problem.
Although the CARES Act did include childcare support, New York receiving $164 million going toward the childcare industry to provide protective equipment and cleaning supplies, the panel argues that while helpful those measures still did not provide adequate relief. The HEROES Act could potentially provide further relief for the care industry, but participants of this forum are less than optimistic about it providing the level relief needed.
The International Labor Organization estimates that three-quarters of unpaid care worldwide is provided by women. In the U.S. women provide 37% more unpaid care work than men on a daily basis. Among care providers in the U.S., Hispanic women do the majority of unpaid care and account for the biggest gap among men and women. Beyond traditional gender roles, this is largely tied to economics; oftentimes men have opportunities to make more money. But generally speaking, even when both parents work full time, women are still taking on more unpaid work even if they are earning more money than the male figure within the household.
There is also a societal tendency which expects care workers to be exceptionally giving. This is highlighted in the fact that even within paid care work positions, there is a fair amount of unpaid work being performed. For example, staying with an elderly person at their doctor’s appointment a couple of hours after the official workday has ended. This is a constant strain within the care industry, and COVID-19 has increased the pressure on this component of unpaid work within the paid care industry.
Additionally, the many racial and ethnic disparities within care work serve as a microcosm of larger racial inequities prevalent in society. For example, in New York, 80% of care workers are women, and a large majority of them are women of color. Furthermore, care workers in New York typically make minimum wage yet are still known to go above and beyond in their roles to ensure the best care is provided, regardless of whether or not it is part of their job description. This existing issue has been pushed to a new level due to COVID-19; now many of our care workers are putting their lives on the line.
Part of the reason that low wages are prevalent within the care sector is the historical association that care work is a “women’s job,” coming naturally and requiring little skillset. This sentiment in the U.S. is compounded by care work being viewed as the responsibility of the individual. The decision to have a family is viewed as a personal choice, therefore the basic needs of childcare are the sole responsibility of the parents, not something to be addressed via larger social safety nets.
New York is facing a particularly troubling dilemma within its care work industry. Despite the fact that a large majority of the workforce is comprised of immigrants, the guidelines that have been released outlining protection measures from COVID-19 are only available in English. This is concerning given that some workers may not yet possess the English language proficiency necessary to fully comprehend these guidelines.
In order to address these strains within the care work industry, political will and national policy are needed. The U.S. Department of Defense provides an exemplary model that could be emulated on a national scale. This government sector presently has one of the best childcare systems available in the U.S., operating on a sliding scale making it accessible to all those within the department that need it. This allows these federal employees to perform their duties with the comfort of this social safety net.
Furthermore, at the local level, immediate state, and county-level funding for care work can have a significant impact on the accessibility needed during this stressful time. Without swift action on the policy level, the issues discussed will continue and have detrimental effects on not only families, but economic recovery as well.
This blog was authored by Jenn Brown, CWE-GAM Communications Assistant
- Published in COVID 19, Expert Dialogues & Forums, Policy, U.S.
COVID-19 AND THE CARE ECONOMY: UN Women calls for immediate action and structural transformation for a gender-responsive recovery
A recent brief from UN Women presents emerging evidence on the impact of the COVID-19 global pandemic on the care economy.
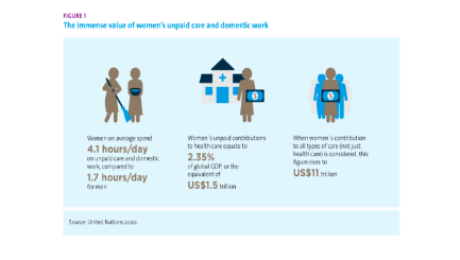
Evidence suggests that the rising demand for care in the context of the COVID-19 crisis and response will likely deepen already existing inequalities in the gender division of labor, placing a disproportionate burden on women and girls. Not only are women over-represented among paid health care workers, girls and women also shoulders the bulk of unpaid care and domestic work that sustains families and communities on a day-to-day basis.
School closures and household isolation across the globe are moving the work of caring for children from the paid economy—schools, day-care centers, and babysitters—to the unpaid economy. So far, 1.27 billion students (72.4 percent) across 177 countries have been affected by school closures (UNESCO). The lack of childcare support is particularly problematic for essential workers, including those in the health sector, who have care responsibilities.
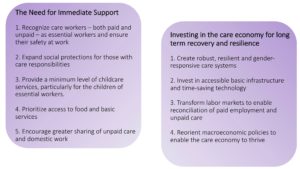
This brief recommends ways to transform care systems now and for the future – both the need for immediate support and the need for sustained investment in the care economy for long term recovery and resilience.
How to Transform Care Systems – Now and for the future
(UN Women, 2020)
Authors/editor(s): Bobo Diallo, Seemin Qayum, and Silke Staab 2020
- Published in COVID 19, Policy Briefs & Reports, UN Women
The Covid-19 Care Penalty
In the U.S., as elsewhere, essential workers have been rightly praised for their willingness to take on additional risk and stress. Their commitment to helping patients, students, and customers face-to-face went beyond the ordinary requirements of earning a paycheck. Yet some essential workers faced more serious risks of infection than others, and differences in pay among them were also significant. The abrupt creation of a new category of workers based on social need, rather than market forces, dramatized an important question: why do we often see a disjuncture between the social value of work and its private, pecuniary reward?
Feminist research addresses this question in a number of ways, emphasizing factors such as employer discrimination, monopoly or monopsony power, and intersectional differences in the relative bargaining power of distinct groups of workers. The distinctive features of care work—intrinsic motivation, emotional skills, team production, and positive spillover effects—have also received attention. Leila Gautham, Kristin Smith and I have been building on previous research on care penalties to show that essential workers in care services (health, education, and social service industries) are paid less than other essential workers (in law enforcement, support and waste services, transportation, agriculture, retail and financial industries) with comparable personal and work characteristics, a pattern with especially costly consequences for women. Low-wage workers such as health aides are especially vulnerable, but care penalties also help explain the vulnerability of doctors and nurses in ways mediated by unique institutional features of the U.S. health care system.
A paper on this research is now under review. Once this process is complete, I’ll come back with more details.
Original blog published on CARE TALK: FEMINIST AND POLITICAL ECONOMY on June 11, 2020. See here for the original posting.
Reposted with permission from Dr. Nancy Folbre from University of Massachusetts Amherst and an expert researcher for the Care Work and the Economy Project within the Rethinking Macroeconomics working group.
- Published in COVID 19, Feminist Economics
Frontline Care Workers in the U.S.
A recent report on Basic Demographic Profile of Workers in U.S. Frontline Industries by the Center for Economic and Policy Research (CEPR) looks at six broad industries, employing grocery store clerks, warehouse workers, bus drivers, and care workers – including nurses, care workers at child care and residential care facilities, as well as household and community service workers.
Based on CEPR’s analysis using the American Community Survey (2014 – 2018), over half of all essential workers in the industries examined are employed in care services. More than a third of these workers are over the age of 50; and before the pandemic, nearly a quarter were living in low-income households and about half lived with a child or a senior at home.
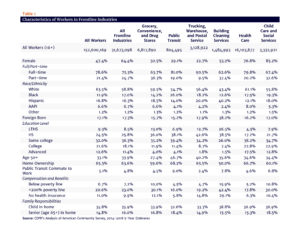
At the national level, women workers are overrepresented in frontline industries. About one-half of all workers are women, but nearly two-thirds (64.4 percent) of frontline workers are women. Women are particularly overrepresented in care-work related industries – Healthcare (76.8 percent of workers) and Child Care and Social Services (85.2 percent).
Black and Hispanic workers, as well as other people of color are also overrepresented in many frontline industries occupations. Black workers are most overrepresented in Child Care and Social Services (19.3 percent of workers). Hispanic workers are especially overrepresented in Building Cleaning Services (40.2 percent). Immigrants are also overrepresented in Building Cleaning Services and in many frontline occupations in other frontline industries.
The report calls on U.S. congress to include important protections for frontline workers in its response to COVID-19 – including comprehensive health-care insurance, paid sick and family leave, free child-care, student loan relief and other labor protections related to workers’ health, safety and immigration status.
About the report:
A Basic Demographic Profile of Workers in Frontline Industries. Hye Jin Rho, Hayley Brown, and Shawn Fremstad. Center for Economic and Policy Research. April 2020.
- Published in Child Care, COVID 19